|
INTRODUCTION :
In 2021 Apr, I decided to finally get around to installing a Linux
'distro' (distribution) with the
MATE desktop environment on an HP 'laptop' computer
that I bought back around 2020 Jan
(at Target for $300, $50 off the regular price of $350).
I decided to install
Ubuntu-MATE on the HP laptop --- for reasons indicated in an
Ubuntu-vs-LinuxMint section below.
I downloaded a '.iso' file (64-bit) from the
Ubuntu-MATE download page, and I used a
'Hybrid-ISO-to-USB-Drive' script of the 'feNautilusScripts'
system at the software site
www.freedomenv.com to put the '.iso' file on a 'USB stick'.
That script uses the 'dd' command to put the '.iso' file
on the USB stick using a command of the form:
sudo dd if=<iso-file-name> of=/dev/sdX bs=1M
Although the Ubuntu-MATE team was about to release the new
Ubuntu-MATE 21.04 (2021 April) release, I decided to use
the 'more mature' Ubuntu-MATE 20.04.2 (2020 April) LTS (Long Term Support)
release, that had been through about 2 updates.
The computer 'specs' of the laptop that I identify as 'HPlaptop01' were as follows:
Model:
HP 15-db0031nr
CPU Processor:
AMD A9-9425 (7th gen, dual core, 3.1GHz, 3.7GHz Max Turbo Frequency, 1MB L2 Cache)
GPU processor: AMD Radeon R5 series (integrated card)
Memory: 4 GB DDR4-1866 SDRAM (1 x 4GB)
Monitor size: 15.6 inches
Monitor resolution: 1366x768 LED LCD (max?)
Hard Disk Drive: 1 TB Toshiba, 5400 RPM SATA
Optical Drive (CD/DVD): DVD writer
USB Type-A ports: 2 USB3.1Gen1 ports (data transfer only) ; 1 USB2.0 port
Video ports: 1 HDMI
Ethernet port: 1 RJ-45 Ethernet 10/100/1000 Gigabit
Wi-Fi: 802.11ac
Bluetooth: 4.2
Battery: 3-cell Lithium ion
Weight: 3.88 lb (1.77 kg)
Dimensions: 0.8 x 14.8 x 9.7-inches (H x W x D, approximate)
Other features: dual speakers, 1 3.5mm headphone/microphone port,
webcam with integrated digital microphone, 1 multi-format SD media card reader,
touchpad with multi-touch gesture support
Operating system: Windows 10 Home 64-bit
Manufacture date: 2019 May ??
A nice set of benchmark results for many CPU's working
in a 'single-thread' mode can be seen at
cpubenchmark.net. You can compare the performance of
the AMD A9 CPU to various low-end to mid-power Intel processors,
such as various models of 'Atom', 'Celeron', 'Pentium', and 'i3'
processors (surprisingly many!).
The AMD A9-9425 CPU had a PassMark rating of 1,355.
This was near the middle of the 'PassMark' performance ratings for
laptop-CPU's --- which ranged from about 3,750 down to about 100.
Ubuntu-MATE rather than LinuxMint-MATE:
I had installed a couple of releases of LinuxMint with the MATE desktop
environment on a couple of Acer 'netbook' computers, back around 2012,
as described on some LinuxMint install pages of this site.
But I found I liked the old Ubuntu-Gnome2 desktop envivironment with
a 'top panel' (strip along the top of the screen) --- with the 'Applications',
'Places', and 'System' drop-down menus --- as well as a 'bottom
panel' (strip along the bottom of the screen) --- that shows icons
representing currently running tasks/windows.
The MATE desktop environment was 'forked' from Gnome2 and has
preserved the 'top-and-bottom' 'thin-panels' design.
Over the 2012 to 2018 time frame, I decided that I would definitely
prefer Ubuntu-MATE rather than LinuxMint-MATE. LinuxMint-MATE eliminates the
MATE 'top panel' in favor of a rather monolithic MS-Windows-like 'Start'
panel (menu) that is initiated by a click on the left of the 'bottom panel'
--- the 'strip' along the bottom of the screen.
I find the MATE 'top panel' allows for faster access to either 'Applications'
or 'Places' (directories of files) or 'System' (computer utilities) ---
instead of presenting all of them when you only need one of these object types.
Following are step-by-step notes on the installation of Ubuntu-MATE 20.04.2
on the 'HPlaptop01' laptop.
TAILORING THE HP-PC BOOT MENU :
(for a Linux install with a 'USB stick')
To get to the
UEFI /
BIOS menu.
By doing web searches on keywords such as
'computer bios uefi menu key hp acer dell',
you can find information on which key to use to get
to the BIOS/UEFI menu on your computer. I found that F10
is typically used on HP laptop computers.
I held down the F10 key --- then I pressed the power-on button.
The 'InsydeH2O Setup Utility' (Rev. 6.0) opened within a
few seconds.
It showed 'toolbar' options with the names:
- 'Main'
- 'Security'
- 'System Configuration'
- 'Exit'
You can use the right and left arrow keys to choose
one of these menu options.
The 'Main' menu consisted mainly of unchangeable text
showing features of the computer, such as the processor type
and amount of memory.
The 'Security' menu provides the option to set an
'Admin' password and a 'Power-On' password.
The 'System Configuration' menu was the main menu that
I needed to access --- to change the 'boot order' of
devices --- to allow my 'USB stick' to be accessed first.
The SysConfig menu included a submenu called 'Boot Options'.
I entered that menu --- via down-arrow and Enter keys.
I left the 'Secure Boot' option at 'Enabled' --- and
the 'Legacy Boot' option at 'Disabled'.
I also left 'USB Boot' and 'CD-ROM Boot' at 'Enabled'
--- and 'Network Boot' at 'Disabled'.
I went down to the section titled 'UEFI Boot Order'
and used F5 and F6 keys to change the default boot order
(that had 'OS Boot Manager' at the top) to the following.
-
USB Diskette on Key / USB Hard Disk
-
Internal CD/DVD ROM Drive
-
USB CD/DVD ROM Drive
-
OS Boot Manager
-
! Network Adapter
(I guess that the exclamation point is there
because the 'Network Boot' option was set to 'Disabled'.)
I also set 'POST Hotkey Delay (sec)' from 0 (zero) to 5
--- in case it would help me get to the BIOS/UEFI menu
more easily. (I used the F5 and F6 keys to change zero to 5.)
I used the F10 key to 'Exit Saving Changes'.
I think this is what happened next
(I did not take detailed notes):
The screen cleared and after about a minute an MS Windows 10
login prompt appeared. I chose 'Shutdown' via an icon at
the bottom-right of the screen.
I was now ready to insert the USB stick --- that contained
the Ubuntu-MATE 20.04 '.iso' file --- 'dd-loaded' onto it.
By the way,
in the course of the installation process described below,
I found that you do not have to go to the BIOS/UEFI menu
to see if 'Secure Boot' is turned on.
You can enter the following command at a terminal prompt.
In my case, where I left 'Secure Boot' enabled, this command
returned the string 'SecureBoot enabled'.
You can use the command 'man mokutil' to get information
on that command.
This BIOS/UEFI-Boot-Menu section is an appropriate place for me
to point out that the 'OS Boot Manager' line was high-lighted,
indicating that you can select that line and press the Enter key
to get a response (shown below).
After I completed the Ubuntu-MATE 20.04 installation, as described
below, I found that when I went back into the Boot-Menu and
clicked on the 'OS Boot Manager' line, it showed me the
following string.
Before I wiped out the Microsoft Windows 10 operating system
with the Ubuntu-MATE operating system, I expect that the
string diplayed would have said something about 'microsoft'
or 'windows10' or the like. I may check this out on a
Windows 10 machine in the future, when I do another
overlay of Microsoft-Windows with Ubuntu.
'LIVE' TEST OF THE DISTRO
(without install to disk):
I did not take detailed notes on the startup into
a 'live' install of Ubuntu-MATE 20.04 --- but here
is roughly what happened.
I put the 'USB stick' (containing the 'hybrid' ISO file)
into a USB slot on the 'HPlaptop01' laptop computer.
I powered back up by a press on the HP laptop power-on button.
I MAY have gotten a 'GNU GRUB' menu that showed options
such as
- Try Ubuntu MATE without installing
- Install Ubuntu MATE
- OEM install (for manufacturers)
- Check disk for defects
I chose to 'Try without installing'. (The following times
are estimates from another Ubuntu install.)
The screen went blank for about 14 seconds.
Then an Ubuntu-MATE logo appeared in the center of the screen
with 5 dots horizontally centered below. One dot at a time would
get brighter than the other 4 ... indicating something was
happening. (I would rather see messages from 'what was happening'.)
At about 54 seconds, the screen went blank again.
At about 80 seconds, the MATE top and bottom panels appeared along
with the desktop background.
At about 90 seconds, the Ubuntu-MATE 'Welcome' window appeared
in the middle of the MATE desktop background.
In a 'live' (in-memory, not-on-disk) try-out of a distro,
I typically like to check if
-
I can use the file manager to examine some directories
-
I can use a web browser to access the internet
-
the latter means I need to make sure I can access
a wireless access point --- especially if I do not
have a WIRED internet connection option.
There were 'Menu' and Firefox icons on the left of the
'MATE top-panel' --- and there was a user's 'Home' icon
on the desktop, by which to access the sub-directories
and files of the user's home directory.
I was able to use the 'Home' icon on the desktop to
verify that the MATE Caja file manager was working well
to allow me to quickly navigate directories.
On the right of the 'top-panel', there is an icon representing
the MATE 'Network Manager' applet.
I clicked on the 'Network Manager' icon to examine its drop-down
menu.
The 'Ethernet network' option line was grayed out and the line
below that line showed 'disconnected'. This was an indication that I
did not have an ethernet cable plugged into the computer because
the hotel where I was did not have a wired-ethernet connection option.
The 'Wi-Fi network' option line was grayed out and the line
below that line showed 'disconnected'.
The disconcerting thing to me is that the hotel's wireless
access point name did not show up under the 'Wi-Fi network'
option line.
In fact, when I clicked on the Firefox icon and started up
Firefox, it was unable to connect to the Firefox site.
I was hoping this 'no-wireless-access-point' problem would
be an easy problem to solve --- so I proceeded to do an
'install-to-disk' of the Ubuntu-MATE 20.04 operating system.
INSTALL DISTRO TO DISK:
SPOILER ALERT:
I encountered two main problems with this install-to-disk :
-
After I answered a login prompt that (appeared on a nice rendering
of the MATE desktop background), the MATE desktop appeared ---
BUT THE MATE DESKTOP APPEARED IN A GARBLED STATE.
The top-and-bottom panels and the drop-down menus --- such as
'Applications' and 'NetworkManager' and 'Shutdown' menus
--- appeared in an UNREADABLE, FRACTURED, STAIR-STEP fashion
on the desktop --- as reported (and shown) at
an Ubuntu-MATE Community forum web page.
Here are three images from that forum page that give an idea of the
'garbling' of the desktop and its menus.
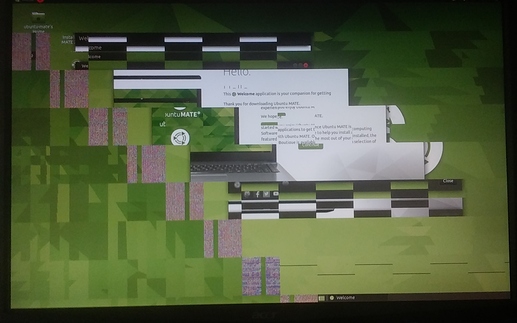
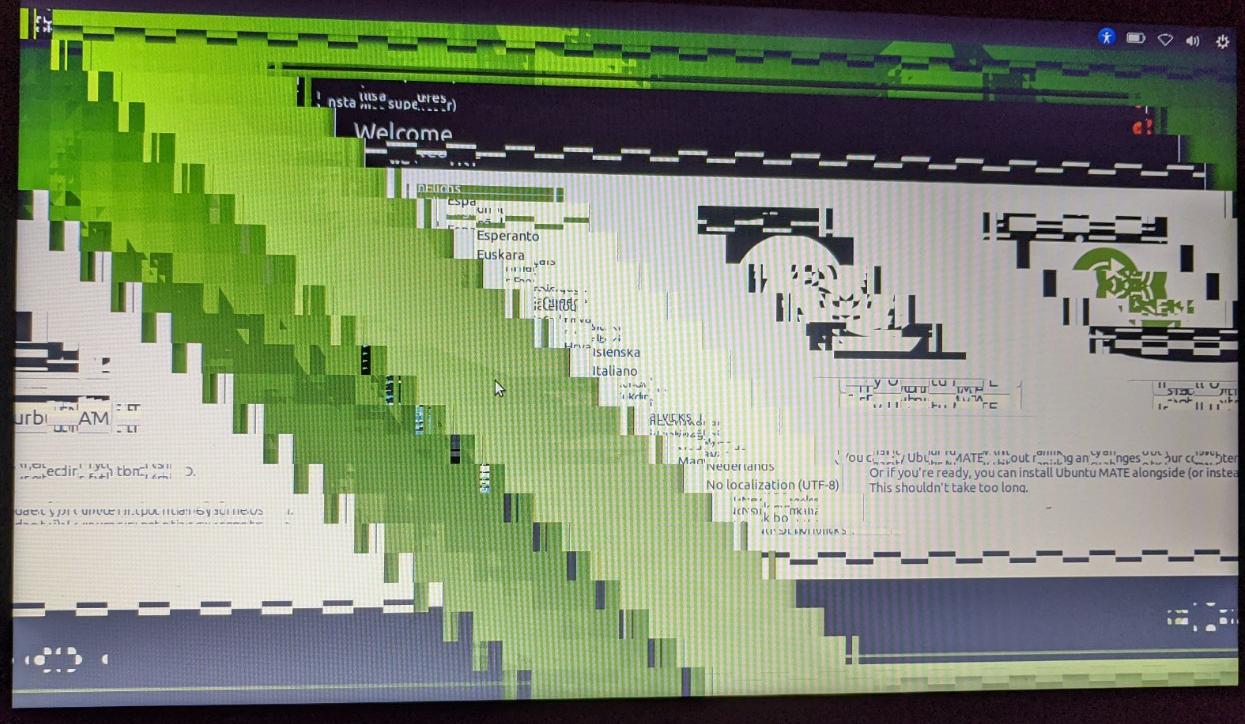
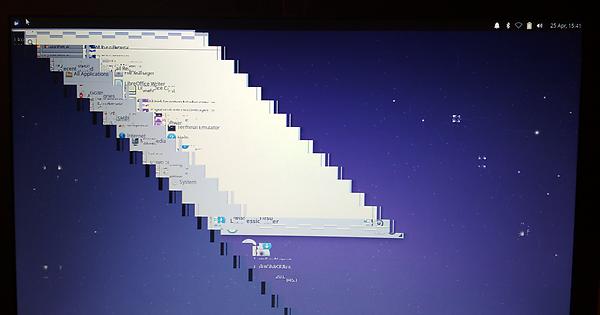
You can click on any of these images to see them
in a separate window where you may be able to enlarge
the images with the 'Ctrl' key & the scroll wheel of a mouse.
I basically worked around (and solved) this problem by opening a
terminal window with key strokes Ctrl-Alt and F2
(to avoid the graphical desktop altogether)
and edit a
Grub config file to add a 'nomodeset' parameter.
(Details below.)
-
After I finally found a solution to get a readable-unfractured desktop,
I found that the NetworkManager app was
not detecting the wireless access points in the area ---
after this 'install-to-disk'.
This was a problem to me, because I was not at home --- where I had
a WIRED-ethernet connection. I was on-vactaion at a hotel with
no wired-ethernet connection option. I needed an internet connection
on this computer so that I could do added-software installs.
After lots of web-searching on this problem,
I found that the Realtek '8821ce' wireless adapter
on this laptop was not supported by the Ubuntu 20.04 system
(neither the Ubuntu-GNOME nor the Ubuntu-MATE flavors).
I found a way to connect my Android cellphone (which WAS able to
connect to the hotel wifi system) to the HP laptop
--- to provide a wireless connection via 'USB Tethering'
--- thanks to a YouTube video on the '8821ce' wireless adapter
problem on Ubuntu 20.04.
Then I was able to install the appropriate '8821ce' wireless
software via a simple command like
as was mentioned briefly on
an 'askubuntu.com' forum web page.
Then I was able to use the wireless connection to install many
software packages (that I often use or that I may someday use)
--- as described in a section below.
(NOTE:
It has been the case in the past that when I cannot find
an answer to an Ubuntu-MATE --- or LinuxMint-MATE --- install
problem on the Ubuntu-MATE --- or LinuxMint-MATE ---
community forum, I can often find a relatively-uncomplicated answer
--- among lots of unnecessarily-complex answers, after hours of web-searching
and reading --- on a 'main Ubuntu' forum such as 'askubuntu.com'.)
Here are some details of the install-to-disk :
Although, in the 'live-install', the Network Manager was not showing
the hotel wireless access point in the drop-down Network Manager menu,
I decided to go ahead and do the install of Ubuntu-MATE 20.04 to disk.
In the 'live' install, I clicked on the desktop icon labelled
'Install Ubuntu MATE 20.04 LTS'.
I got the usual prompts for options like the following
(not necessarily in the following order).
-
language and keyboard
(I took the 'English(US)' defaults.)
-
a time zone
(I took the 'New York' - i.e. U.S. East Coast - default.)
-
whether to install along with Windows10 already on
the disk OR install Linux on the entire disk
(I chose to use the entire disk; I had no files
in the Windows10 installation that I wanted.)
-
a 'Normal' installation or a 'Minimal' installation
(I took 'Normal' which added a lot of apps like
Libre Office and various media apps.)
-
Got another panel that prompted for computer-name (hostname),
user-name, user-ID (login ID), and password (twice).
-
I checked a box to 'Require password to log on'.
Then copying and installing of files occurred for about
20 minutes.
When the installation was complete, I got a nice looking
green-MATE desktop with a small window prompting for my
passord. I entered the password I had just specified and
pressed Enter.
The Garbled Desktop Problem:
Here is where I got the shock that the desktop was shown
as a 'garbled mess' --- like the images above.
I got my cell phone and started doing web searches on
keywords such as
'ubuntu mate 20.04 video problem after install to disk'
I finally found the
Ubuntu-MATE Community forum web page that included the
'garbled images' above.
That forum page is a rather long page with many posts --- and the bottom of
the page gets into a different video/monitor problem that should
have been reported in a separate thread.
LUCKILY the following May 2020 post from 'ilvipero' gave me a hint on
how to find a workaround and solution.
START-QUOTE:
.... I found a temporary workaround for Ubuntu MATE.
-
Boot live ISO, select safe graphics. Complete installation and shut down.
-
On first boot, Hit "Esc" key to show GRUB menu, then "e" to edit,
insert 'nomodeset' at the end of the line that starts with
"linux /boot/vmlinuz...". Press F10 to boot.
-
Login and open "MATE Tweak".
-
Select the third item from left panel: "Windows".
-
In the Window Manager, switch to "Marco (No compositor)".
-
Reboot ('nomodeset' will not be persistent so next boot
is normal graphics mode).
-
Enjoy.
Please note this is a temporary workaround so we can keep using
Ubuntu MATE until a permanent fix is found.
Once that is done, we can switch back to "Marco (Adaptive compositor)".
END-QUOTE:
UNFORTUNATELY, I was disappointed that at the Grub 2.04 command
prompt, when I keyed in 'e' or 'edit', I got an invalid command
message.
Maybe there is a way to (temporarily) edit the Grub 2.04 boot
parameters. Maybe I am missing something to get into edit mode.
BUT I was able to solve the problem by doing
the following steps --- based on my knowledge from monitor
problems with some previous Linux installs that required
using the 'nomodeset' parameter in a Grub config file to
(permanently) get around a 'black screen' problem after
an install-to-disk.
Here is what I did to 'permanently' solve the 'garbled-desktop'
problem.
-
At the garbled desktop, I used the Ctrl-Alt and F2 keys
to get a terminal screen in which to enter commands.
I refreshed my knowledge that I had to edit the '/etc/devault/grub'
file. I changed the line
TO
(I removed the 'quiet splash' parameters because I like to
see the messages coming from the boot up processes ---
rather than watching a blank screen with an Ubuntu logo
for almost 2 minutes at boot up.)
I am not proficient at using the 'vi' editor, so I used
the more user-friendly 'nano' editor by entering the
following commands at the terminal command prompt.
-
The comments at the top of that 'grub' file pointed
out that you need to run the 'update-grub' command to
put your changes into the file '/boot/grub/grub.cfg'.
So, after exiting 'nano', I used the command
-
Then I used the command 'shutdown now' to power down the laptop.
-
I started up the laptop and was now able to log into a
readable, ungarbled desktop.
I used 'MATE Tweak' to change the 'Window Manager' option from
'Marco (Adaptive compositor)' to 'Marco (No compositor)'.
I got to these 'MATE Tweak' options by using the following
sequence in the 'System' menu.
Thus ends my solution to the 'garbled desktop' problem.
NOTE:
The Ubuntu-MATE development team probably could have saved
a lot of people from having the 'garbled desktop' problem
by making 'Marco (No compositor)' the default window manager
--- instead of 'Marco (Adaptive compositor)'.
I am leaving 'nomodeset' in my Grub config file on this laptop.
And I am leaving the MATE 'Window Manager' option set at
'Marco (No compositor)' rather than 'Marco (Adaptive compositor)'
--- unless I find a compelling reason to change that setting.
The No-Wireless-Access-Points Problem:
Now that I had the garbled-desktop problem fixed, I wanted
to start setting various 'preferences' in Caja and the desktop
--- and then start installing applications that I like to use
--- from the 'Software Boutique' and by other methods.
But I needed an internet connection to get software files
from Ubuntu repositories and from various web sites
(for example: Seamonkey web browser, Epson 'imagescan') .
I had no WIRED-connection at this hotel. And the 'Network Manager'
was not showing the hotel's wireless access point.
To make a long story short, via web searches, I finally
found this
'askubuntu.com' forum web page --- titled
'Wi-Fi not working on Lenovo Thinkpad E570 (Realtek RTL8821CE)'.
This is a rather long page offering some rather complex
solutions involving downloading some 'git' files of
'tomaspinho'.
LUCKILY 'alexeypetrenko', in a Jul 2020 post, provided the
following solution that requires running one command.
START-QUOTE:
Ran in the same problem today with ubuntu 20.04.
Reading through https://github.com/tomaspinho/rtl8821ce carefully I found out that there is a ready made package by Canonical: rtl8821ce-dkms
Installation boils down to:
That's it. Nothing else. After reboot everything just works.
END-QUOTE:
Using the 'USB Tethering' to my cellphone, I was able to
run that 'apt install' command and rebooted. When I logged back into the
HP laptop, the 'NetworkManager' now showed the hotel's access point.
By the way,
I was able to do the 'USB Tethering' on my Android cellphone
by using
and set the 'USB tethering' button ON.
I plugged a USB cord from the cellphone into a USB socket
on the laptop. The 'Network Manager' applet recognized
the cellphone connection almost immediately. I had my
internet connection.
In the process of researching this wireless-access-not-working problem,
I found that the '.ko' (kernel object) files that serve as 'drivers'
for Realtek wireless adapters are located in a directory like
where 5.8.0 is the Linux kernel release in Ubuntu-MATE 20.04.
The '.ko' files were in the following subdirectories of the
'rtlwifi' directory --- with the same filenames as these directory names.
- rtl8188ee
- -------
- rtl8192c
- rtl8192ce
- rtl8192cu
- rtl8192de
- rtl8192ee
- rtl8192se
- -------
- rtl8273ae
- rtl8273be
- rtl8273com
- -------
- rtl8821ae
Presumably, if you have one of these
Realtek wireless adapters on
your computer, then Ubuntu 20.04 would support it 'out of the box'.
There were '.ko' files in other subdirectories of the 'wireless' directory
that provided drivers for
Broadcom and
Atheros wireless adapters.
SETTING PREFERENCES:
I did not need an internet connection to set a lot of my
preferences for the Caja file manager and for various
desktop options such as appearance of windows.
So, until I found a solution to the internet connection
problem, I could proceed to set various preferences.
Rather than go into detail on various preferences that
I set, I will refer to my other web pages on past
installations of Ubuntu-MATE (16.04 and 18.04) and LinuxMint-MATE ---
and even old installations of Ubuntu-Gnome2 (9.10, 'Karmic Koala') ---
in which I list many of the preferences that I set.
I WILL mention two main things that I like to change in MATE.
1) Top-panel menus:
I like to intall the 'Classic Menu' (the 'Applications',
'Places', 'System' menu options) on the 'top-panel'.
You can right-click on the 'top-panel' and choose the
'Add to panel ...' option.
A window opens and you can scroll down and select the
'Classic Menu' option and click on the 'Add' button.
When the Applications-Places-System triplet appears on the
'top-panel', you can right-click on that 'icon' and
use the 'Move' and 'Lock to panel' options to place
the triplet where you want it on the 'top-panel'.
2) Files View:
I like to change the files view in the Caja file manager
from 'Icon View' to 'List View' --- because I am frequently
dealing with directories with more than 100 files ---
not easily managed with icons spread all over
(and out of sight on) a Caja file manager window.
To change to 'List View', you can open the Caja file
manager --- for example, on your home directory.
On the Caja file manager toolbar, select 'Edit'
and then select 'Preferences' on the drop-down menu
A 'File Management Preferences' window appears,
in which you can change a 'Default View' option
from 'Icon View' to 'List View'.
3) Other:
There are many other preferences that I set ---
especially preferences in web browsers such
as Seamonkey and Firefox. Some of those
preferences may be described in my other
'Ref-Info > Computer' web pages.
INSTALLING APPS:
Adding app icons to the MATE-top-panel:
Now that I had an 'ungarbled' desktop, I added app icons to the
'MATE top panel' by right-clicking on various 'Applications'
menu drawers and choosing the option 'Add this launcher to panel'.
For apps that were not in the 'Applications' menu, I knew that I could
use the Ubuntu-MATE 'Software Boutique' or the 'Synaptic package manager'
to install more apps. I 'set up' about 50 apps as follows.
I installed the 'Synaptic package manager' from the 'Software Boutique'.
From the 'Applications' sub-menus, I added the following apps,
as icons, to the top panel --- apps that I have found convenient
to have in the top panel in my other Gnome2-Nautilus and
MATE-Caja installations.
I made the following groups of icons in the top panel.
Handy utilities:
-
MATE-Terminal 1.24.0
(came with Ubuntu-MATE)
-
MATE-Calculator 1.24.0
(came with Ubuntu-MATE)
-
MATE-SystemMonitor 1.24.0
(came with Ubuntu-MATE)
Text Editors:
-
MATE Pluma Text Editor 1.24.0
(came with Ubuntu-MATE)
-
Scite Text Editor 4.3.0
(installed via Synaptic)
-
Geany 1.36
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
Web Browsers:
-
Seamonkey 2.53.7
(installed from file of the
Seamonkey web site)
-
Firefox 85.0.1
(came with Ubuntu-MATE)
-
Chromium 85.0.4183.83
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
(Chromium was a bulky
'Snap' installation
that requires a constantly running 'snap' demon.
If I had known that, I would not have installed it.
I am not alone in being of the opinion that Ubuntu developers
should NOT be trying to SNEAK 'snap' installs upon us.)
-
Brave 1.23.71
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
Vivaldi 3.7.2218.58
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
Mail client:
Internet File transfer utility:
Capture utilities:
-
Audacity audio recorder/editor 2.3.3
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
MATE-screenshot 1.24.0
(came with Ubuntu-MATE)
-
Kazam screen video recorder 1.4.5
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
Simple Screen Recorder 0.3.11
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
Cheese webcam recorder 3.34.0
(came with Ubuntu-MATE)
-
Peek animated GIFs of screen 1.5.1
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
Scanner utilities:
-
Epson 'imagescan' 3.65.0
(installed from file an
Epson web site)
In fact, one of my main reasons for setting up this HP laptop is
to use it with an Epson scanner. I want to make this HP laptop
a 'dedicated' scanning workstation -- for digitizing slides and
text --- and for some French-to-English geneological
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) tasks.
-
'Document Scanner' 3.36.3
(also known as 'simple-scan', from Canonical)
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
Other apps installed (not on top-panel):
I have a lot of
Nautilus/Caja scripts that use the 'ImageMagick'
'convert' program, so I wanted to install the 'imagemagick'
system of utilities.
The FE Nautilus/Caja scripts are designed to be used in the Caja file manager ---
via the right-click popup menu of Caja --- and the 'Scripts' option
(that appears just below the 'Open with' option) in that popup menu.
I also wanted to install the GUI
'mtpaint' image editor utility.
I did not need it in the top-panel, because I hardly ever
need to start it without specifying an image filename.
I would usually want to select an image file in the Caja
file manager and then apply the 'mtpaint' program to the file
--- by a right-click on the image filename and using the
'Open with ...' option of the Caja popup menu.
Below is a list (in alphabetical order) of the
apps that I installed --- but I do not use them
enough to need to access them quickly via an
icon on the 'top panel'.
You can click on the software-name links to go to a web
page that describes the software.
-
Asunder 2.9.5
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
Blender 2.82.a
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
bless hex editor 0.6.0-7
(installed via 'Synaptic')
-
Brasero 3.12.2
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
Codecs Pack
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
(Different from 'ubuntu-restricted-extras', shown below??)
-
EasyTAG 2.4.3
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
gifsicle 1.92-2
(installed via 'Synaptic')
-
GIMP 2.10.18-1
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
Gip 1.7.0
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
gLabels 3.4.1
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
gnome-terminal 3.36.2
(installed via 'Synaptic')
-
gnuplot 5.2.8
(installed via 'Synaptic')
-
Gparted 1.0.0
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
Handbrake 1.3.1
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
ImageMagick 8:6.9.10.23
(installed via 'Synaptic')
-
Inkscape 0.92.5
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
kdenlive 4:19.12.3
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
mencoder 2:1.3.0
(installed via 'Synaptic')
-
mplayer 2:1.3.0
(installed via 'Synaptic')
-
mtpaint 3.40-3
(installed via 'Synaptic')
-
plotdrop 0.5.4-1
(installed via 'Synaptic')
-
pngcrush 1.8.13
(installed via 'Synaptic')
-
Psensor 1.1.5
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
Pulse Audio Volume Control 1:13.99.1
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
Rapid Photo Downloader 0.9.23a1
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
Scribus 1.5.5
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
smplayer
(installed via 'Synaptic')
-
Sound Converter 3.0.2-2
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
Tcl 8.6
(installed via the 'sudo apt install tcl')
-
Telegram messaging app 2.1.7
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
tesseract 4.1.1-2
(installed via 'Synaptic')
-
Tex Works 0.6.3-3
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
Tk 8.6
(installed via the 'sudo apt install tk')
-
totem (aka GNOME Videos) 3.34.1-2
(installed via 'Synaptic')
-
ttf-mscorefonts-installer 3.7
(installed via 'Synaptic')
-
ubuntu-restricted-extras 67
(installed via 'Synaptic')
-
VLC 3.0.9.2
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
Wire secure collaboration 3.24.2939
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
-
Wireshark 3.2.3
(installed via the 'Software Boutique')
Since the software repositories for the 20.04 release of Ubuntu-MATE
will only be supported until about 2023, I wanted to try to anticipate
most of the programs that I might want to use.
I will probably never use many of these programs --- that I installed
on this computer. Maybe I will use some of them eventually ---
but probably on a desktop computer.
Some of the programs in the 'Software Boutique' that I did NOT
install, but I might want to install someday were :
I may also wish to install the
Pale Moon web browser someday --- because it has an icon on
its toolbar that you can use to quickly turn Javascript interpretation
OFF and ON.
This can be handy when you are on a web site that is popping up
annoying ads or phony windows that tell you (on a Linux machine)
that your Microsoft Windows operating system has been infected
with a virus.
You can simply turn OFF Javascript and reload the page.
In addition to all the 'binary' executables above, I installed
my script-executables from
freedomenv.com.
Specifically, I installed
I set up the startup scripts of 'tkGooies' and 'xpg' and 'feColorSelect'
and 'feFontSelect' so that they could be executed by clicking on a
desktop icon for each of them.
EVEN MORE APPS INSTALLED:
(28 Apr 2021 update)
A few nice things about the Synaptic GUI package manager:
-
Synaptic has a 'search' option by which you can search
for apps whose name or description contains user-specified
keywords.
-
Synaptic manages thousands of apps --- small and large
--- command-line and GUI.
-
Synaptic will install almost any app you choose within 15
to 30 seconds.
For example, I wanted to search for apps that might help
with doing scanning of documents (esp. with Epson scanners)
and to help with doing OCR (Optical Character Recognition).
So I wanted to do searches on keywords like 'scanner' and
'epson' and 'ocr'.
Also, I wanted to search for apps that would allow for
viewing or creating or editing 3D models --- such as
models of molecules, in addition to models of objects
such as vehicles or people.
So I wanted to do searches on keywords like '3d'.
And I wanted to do searches on keywords like 'audio' and 'video'
and 'image' and 'camera' and 'edit' and 'play'.
Following are about 50 'apps' that I chose to install
using Synaptic and various search terms.
Scanning & OCR apps:
-
gimagereader 3.3.1
Graphical GTK+ front-end to tesseract-ocr.
'gImageReader' is a simple GTK+ front-end to tesseract-ocr.
Tesseract is probably the most accurate open source optical character
recognition (OCR) software and can recognize text in over 60 languages.
'gImageReader' supports automatic page layout detection but the user
can also manually define and adjust the recognition regions.
It is possible to import images from disk, scanning devices,
clipboard and screenshots. 'gImageReader' also supports multipage
PDF documents.
Recognized text is displayed directly next to the image and
basic text editing including search/replace and removing
of line breaks is possible.
Spellchecking for the output text is also supported
if the corresponding dictionaries are installed.
-
ocrmypdf 9.6.0
Add an OCR text layer to PDF files.
'OCRmyPDF' generates a searchable PDF/A file from a regular PDF
containing only images, allowing it to be searched.
It uses the Tesseract OCR engine and so supports all the languages
that Tesseract does.
Some other main features:
* Places OCR text accurately below the image to ease copy / paste
* Keeps the exact resolution of the original embedded images
* When possible, inserts OCR information as a lossless operation
without rendering vector information
* Keeps file size about the same
* If requested deskews and/or cleans the image before performing OCR
* Validates input and output files
* Provides debug mode to enable easy verification of the OCR results
* Processes pages in parallel when more than one CPU core is
available
* Battle-tested on thousands of PDFs, a test suite and continuous
integration.
-
xsane 0.999
Featureful graphical frontend for SANE (Scanner Access Now Easy).
'xsane' can be run as a stand-alone program or through the GIMP image
manipulation program.
In stand-alone mode, 'xsane' can save an image to a file in a
variety of image formats, serve as a frontend to a fax program,
or send an image to a printer.
SANE stands for "Scanner Access Now Easy" and is an application
programming interface (API) that provides standardized access to any
raster image scanner hardware (flatbed scanner, hand-held scanner,
video- and still-cameras, frame-grabbers, etc.).
The SANE standard is free and its discussion and development are
open to everybody. The current source code is written to support
several operating systems, including GNU/Linux, OS/2, Win32 and
various Unices and is available under the GNU General Public License
(commercial applications and backends are welcome, too, however).
-
yagf 0.9.5
Graphical interface for cuneiform and tesseract.
YAGF is a graphical interface for cuneiform and tesseract text recognition
tools on the Linux platform.
With YAGF you can scan images via XSane, import pages from PDF documents,
perform images preprocessing and recognize texts using cuneiform from
a single command centre.
YAGF also makes it easy to scan and recognize several images sequentially.
CAMERA apps:
IMAGE making/editing/viewing apps:
-
gnome-paint 0.4.0-7
Simple, easy to use paint program for GNOME.
'gnome-paint' is a program inspired by MS Paint and designed for
GNOME (and maybe other) desktop environment. It could be used to
manipulate images in a very simple way. With a very friendly
user interface, gnome-paint is easy to get started for new users.
-
gtkmorph 20140707
Digital image warp and morph (gtk).
'gtkmorph' loads, saves, warps, and dissolves images, and loads, saves,
creates, and manipulates control meshes which determine the warping.
'gtkmorph' is a GUI for libmorph, using GTK+. It has many features, as the
support for making movies automatically (it needs extra packages).
-
hugin 2019.2.0
Panorama photo stitcher - GUI tools.
'Hugin' is a panorama photo stitching program. Essentially, Hugin is a
GUI frontend for Panorama Tools.
Stitching is accomplished by using several overlapping photos taken
from the same location, and using control points to align and
transform the photos so that they can be blended together to form
a larger image.
Hugin allows for the easy creation of control points between two images,
optimization of the image transforms, and much more.
This package includes the following graphical interfaces, using the
command-line tools provided in the hugin-tools package:
* hugin - Hugin panorama creator.
* hugin_stitch_project - Hugin batch stitcher.
* PTBatcherGUI - Batch controller for the stitching process.
* calibrate_lens_gui - Lens calibration tool.
-
mypaint 2.0.0-2
Paint program for use with graphics tablets.
'MyPaint' is a pressure- and tilt-sensitive painting program which
works well with Wacom graphics tablets and other similar devices.
It comes with a large brush collection including charcoal and ink to
emulate real media, but the highly configurable brush engine allows
you to experiment with your own brushes and with not-quite-natural painting.
-
pencil2d 0.6.4
Create hand-drawn animation using both bitmap and vector graphics.
'Pencil2D' is an animation/drawing software for Mac OS X, Windows, and
Linux. It lets you create traditional hand-drawn animation (cartoon) using
both bitmap and vector graphics.
The basic features of Pencil2D are:
+ layers support (separated layers for bitmap, vector and sound part)
+ bitmap drawing
+ vector drawing
+ sound support
-
rgbpaint 0.8.7-6
Simple pixel-based painting program.
This package provides the simplified painting program 'rgbPaint',
a spin-off from mtPaint by the same authors. Light on dependencies,
it can edit and save images in ICO, JPEG, or PNG format only,
though it can also read GIF, PCX, SVG, TGA, and TIFF formats.
The user interface is intentionally kept simple, without drop-down
menus. Ten brushes are provided, and a palette of twenty colors,
each of which can be replaced from a color blender.
The available actions are painting, filling, and area selection.
The program can also start by taking a screen snapshot to use as
the initial image.
Originally aimed at the OLPC (One Laptop Per Child) initiative,
'rgbPaint' works well with the Sugar desktop environment -
especially with a graphics tablet; even young children can
quickly master it to produce true brushwork!
-
xaos 3.5
Real-time interactive fractal zoomer.
'XaoS' allows you to zoom and pan around a fractal in
real time. It can display the animated fractals in graphical
or even plain text mode.
'Xaos' displays the Mandelbrot set or many other fractals and
allows you to zoom smoothly into the fractal. Various coloring
modes are provided for both the points inside and outside the
selected set. In addition, switching between Mandelbrot and Julia
fractal types is provided.
Other features include autopilot mode, palette changing,
image saving, fractal inversion, filters, and a built in fractal
tutorial.
3D apps:
-
fraqtiv 0.4.8-11
Draws Mandelbrot and Julia fractals.
'Fraqtive' is a program for drawing Mandelbrot and Julia fractals.
It uses a very fast algorithm and generates high quality, smooth
images.
It is fully interactive, allowing for real-time mouse
navigation and dynamic generation of the Julia fractal preview.
OpenGL-rendered 3D view of the fractals is also supported.
-
fstl 0.9.3-1
Viewer for '.stl' files.
'fstl' is a viewer for '.stl' files commonly used in stereolithography,
rapid prototyping, 3D printing and CAM.
It is optimized to quickly load and render very high-polygon models.
-
g3dviewer 0.2.99.5
3D model viewer for GTK+
'G3DViewer' is a 3D file viewer for GTK+ supporting a variety
of file types by using the LibG3D plugin facility.
Models can be inspected and rendered using OpenGL. Rendering options
include wireframe rendering, shadows, isometric view,
specular lightning, and textures.
See 'libg3d-plugin*' for supported formats.
-
garlic 1.6-3
Garlic is written for the investigation of membrane proteins. It may be
used to visualize other proteins, as well as some geometric objects.
This version of garlic recognizes PDB format version 2.1. Garlic may
also be used to analyze protein sequences.
It only depends on the X libraries, no other libraries are needed.
Features include:
- The slab position and thickness are visible in a small window.
- Atomic bonds as well as atoms are treated as independent drawable
objects.
- The atomic and bond colors depend on position. Five mapping modes
are available (as for slab).
- Capable to display stereo image.
- Capable to display other geometric objects, like membrane.
- Atomic information is available for atom covered by the mouse
pointer. No click required, just move the mouse pointer over the
structure!
- Capable to load more than one structure.
- Capable to draw Ramachandran plot, helical wheel, Venn diagram,
averaged hydrophobicity and hydrophobic moment plot.
- The command prompt is available at the bottom of the main window.
-
gmsh 4.4.1
Three-dimensional finite element mesh generator,
'Gmsh' is a 3D finite element grid generator with a build-in CAD engine
and post-processor.
Its design goal is to provide a fast, light and user-friendly meshing
tool with parametric input and advanced visualization capabilities.
'Gmsh' is built around four modules: geometry, mesh, solver and
post-processing. The specification of any input to these modules is
done either interactively using the graphical user interface or
in ASCII text files using Gmsh's own scripting language.
-
mandelbulber 2.20
3D fractal renderer and animator.
'Mandelbulber2' is a ray-tracing application for drawing three-dimensional
fractals, like Mandelbulb, Mandelbox, Julia, trigonometric, hypercomplex
or IFS fractals.
It is highly customizable and features complex shading algorithms (among
the others there are shadows, depth of field, ambient occlusion).
'Mandelbulber2' is also able to produce animations and has a simple
built-in 3D navigator for exploring the fractals.
-
meshlab 2020.03
System for processing and editing triangular meshes.
'Meshlab' is an open source, portable, and extendible system for the
processing and editing of unstructured 3D triangular meshes.
The system is aimed to help the processing of the typical not-so-small
unstructured models arising in 3D scanning, providing a set of tools for
editing, cleaning, healing, inspecting, rendering and converting this kind
of meshes.
'Meshlab' can read files in these formats: PLY, STL, OFF, OBJ, 3DS, COLLADA
and PTX. It can write PLY, STL, OFF, OBJ, 3DS, COLLADA, VRML, and DXF.
-
mm3d 1.3.12
OpenGL based 3D model editor.
'mm3d' is an OpenGL based 3D model editor that works with triangle-based
models.
'mm3d' supports multi-level undo, skeletal animations, simple texturing,
scripting, command-line batch processing, and a plugin system for adding new
model and image filters. Complete online help is included. It is designed to
be easy to use and easy to extend with plugins and scripts.
'mm3d' supports the following 3d files: MilkShape (ms3d), Wavefront (obj),
LightWave 3d Object (lwo), Quake 2 model (md2), Quake 3 model (md3),
Caligari trueSpace (cob), and AutoCAD (dxf).
-
povray 3.7.0.8-4 (including doc, examples, includes)
Persistence of vision raytracer (3D renderer).
'POV-Ray' is a full-featured ray tracer. Ray tracers simulate objects
and light sources of the real world to calculate photorealistic, computer
generated images.
Because of the nature of ray tracing, this process is
quite CPU-intensive, at the benefit of more realistic images compared to
real time rendering techniques. For example, in POV-Ray, you can model a
glass prism, and you will see a spectrum in the resulting image.
'POV-Ray' by itself is a command-line utility that will take scene
descriptions, written in a special easy-to-understand language, to
produce ray-traced images (or even a sequence of images, for animations).
You can either write those scene-descriptions by hand, or use external
tools to generate (parts of) the scene.
-
qutemol 0.4.1
Interactive visualization of macromolecules.
'QuteMol' is an interactive, high quality molecular visualization
system.
'QuteMol' exploits the current GPU capabilities through OpenGL shaders
to offer an array of innovative visual effects. QuteMol visualization
techniques are aimed at improving clarity and an easier understanding
of the 3D shape and structure of large molecules or complex proteins.
'Qutemol' uses advanced OpenGL techniques and might not work correctly
with all video cards and drivers.
Features QuteMol offers include:
* Real time ambient occlusion
* Depth aware silhouette enhancement
* Ball-and-stick, space-filling and liquorice visualization modes
* High resolution antialiased snapshots for creating publication
quality renderings
* Automatic generation of animated gifs of rotating molecules for
web page animations
* Interactive rendering of macromolecules (>100k atoms)
'QuteMol' reads PDB files as input.
-
rasmol 2.7.6.0
Visualization of biological macromolecules.
'RasMol' is a molecular graphics program intended for the visualisation
of proteins, nucleic acids and small molecules. The program is aimed at
display, teaching and generation of publication quality images.
'RasMol' reads in a molecule coordinate file and interactively displays
the molecule on the screen in a variety of colour schemes and molecule
representations. Currently available representations include depth-cued
wireframes, 'Dreiding' sticks, spacefilling (CPK) spheres, ball and stick,
solid and strand biomolecular ribbons, atom labels and dot surfaces.
Supported input file formats include Protein Data Bank (PDB), Tripos
Associates' Alchemy and Sybyl Mol2 formats, Molecular Design Limited's
(MDL) Mol file format, Minnesota Supercomputer Center's (MSC) XYZ (XMol)
format, CHARMm format, CIF format and mmCIF format files.
This package installs two versions of RasMol, rasmol-gtk has a modern
GTK-based user interface and rasmol-classic is the version with the old
Xlib GUI.
-
raster3d 3.0-4
.
Tools for generating images of proteins or other molecules.
'Raster3D' is a set of tools for generating high quality raster images
of proteins or other molecules.
The core program renders spheres, triangles, cylinders, and
quadric surfaces with specular highlighting, Phong shading,
and shadowing.
'Raster3D'uses an efficient software Z-buffer algorithm which is
independent of any graphics hardware.
Ancillary programs process atomic coordinates from PDB files into
rendering descriptions for pictures composed of ribbons,
space-filling atoms, bonds, ball+stick, etc.
'Raster3D' can also be used to render pictures composed in
other programs such as Molscript in glorious 3D with highlights,
shadowing, etc.
Output is to pixel image files with 24 bits of color information per pixel.
-
view3dscene 3.18.0-3
VRML / X3D browser, and a viewer for other 3D model formats.
'view3dscene' is a viewer for many 3D model formats:
- X3D
- VRML (1.0 and 2.0, aka VRML 97)
- Collada
- OpenInventor
- 3DS
- MD3
- Wavefront OBJ
- Videoscape GEO
- KAnim (Castle Game Engine animations)
Various navigation modes are available, like Examine, Walk (with gravity), Fly.
Collision detection is done. Models can be animated and interactive. Many
graphic effects are possible, thanks to using Castle Game Engine underneath.
'view3dscene' may also be used to convert many 3D model formats to X3D
(in classic and XML encoding).
This 'view3dscene' package includes also a command-line
'tovrmlx3d' program, that performs the same conversions as 'view3dscene',
but doesn't use X or OpenGL (so it's nice to use in scripts to convert
3D models in batch mode).
-
whitedune 0.30.10-2
Graphical VRML97/X3D viewer, editor, 3D modeller and animation tool.
'Whitedune' can read VRML97 files, display and let the user change the
scenegraph and all fields of all nodes.
The most powerful 3D modelling features of 'whitedune' support the
VRML97 Amendment1 style NURBS nodes and Superformula based PROTOs.
This is mainly convenient for building some rounded shapes.
'Whitedune' supports some 3D inputdevices like joysticks, gamepads
or all devices supported via the Xinput protocol and also quadbuffer stereo
visuals.
-
xfractint 20.4.10-2
UNIX-based fractal generator.
Generate Mandelbrot, Julia, IFS, and many more fractals in 2D and 3D,
including those you design yourself.
Version 19 supports arbitrary precision which allows zooming
to a depth of 10^1600, as well as generation of random dot stereograms.
AUDIO apps:
-
audacious 3.10.1
Small and fast audio player which supports lots of formats.
'Audacious' is a fork of 'beep-media-player' which supports Winamp skins
and many codecs.
In the default install, the following codecs are supported:
* MP3
* Ogg Vorbis / Theora
* AAC and AAC+
* FLAC
* ALAC
* Windows Media (WMA)
* WAVE
Additionally, 'Audacious' is extendable through plugins, and contains
other useful features like LIRC support. Support for many more codecs
can also be added through plugins.
This package contains the core player and its localization.
-
cutmp3 3.0.1
Small and fast command line MP3 editor.
'cutmp3' is a small and fast command line MP3 editor. It lets you select
sections of an MP3 interactively or via a timetable and save them to
separate files without quality loss.
'cutmp3' uses 'mpg123' for playback and works with VBR files and even
with files bigger than 2GB.
Other features are configurable silence seeking and ID3 tag seeking,
which are useful for concatenated mp3s.
-
eyed3 0.8.10
Display and manipulate id3-tags on the command-line.
A command-line editor to add/edit/remove ID3-tags on mp3 files.
It supports version 1.0,1.1,2.3 and 2.4 of the ID3 standard.
Additionally it displays some information about the file
such as length and bitrate from an MP3 file.
-
faad 2.9.1-1
Freeware Advanced Audio Decoder player.
'FAAD2' is the fastest ISO AAC audio decoder available. FAAD2 correctly
decodes all MPEG-4 and MPEG-2 MAIN, LOW, LTP, LD and ER object type AAC
files.
This package contains a command line interface to play AAC or MP4 files.
-
playmidi 2.4
MIDI player.
'Playmidi' is a MIDI file player that will play back using FM, GUS,
SoundBlaster or external MIDI. It also supports Creative Music Files
(CMF), Microsoft RIFF (RMI) files and large MIDI archives from games
such as Ultima 7.
The player may be used with a text interface or a graphical interface.
-
qmmp 1.3.1
Feature-rich audio player with support of many formats.
Qmmp is feature-rich audio player with support of many formats.
It is written in Qt.
Supported formats:
- MPEG1 layer 2/3
- Ogg Vorbis
- Ogg Opus
- Native FLAC, Ogg FLAC
- Musepack
- WavePack
- tracker modules (mod, s3m, it, xm, etc)
- ADTS AAC
- CD Audio
- WMA, Monkey's Audio (and other formats provided by FFmpeg library)
- PCM WAVE (and other formats provided by libsndfile library)
- midi
- SID
- chiptune formats (AY, GBS, GYM, HES, KSS, NSF, NSFE, SAP, SPC, VGM, VGZ,
VTX)
DSP effects:
- BS2B effect
- sample rate converter
- LADSPA effects
- extra stereo
- crossfade
Audio output through:
- ALSA
- OSS
- PulseAudio
- JACK
- QTMultimedia
- Icecast
Other features:
- XMMS and Winamp 2.x skins support
- 10-band equalizer
- MP3, Vorbis, AAC, AAC+ streams support
- mms support
- MPRIS (1.0 and 2.0)
- removable device detection (via HAL or UDisks)
- video playback via Mplayer
- lyrics (using lyrics.wikia.com)
- cover art support
- CUE sheet support
- embedded CUE support (for FLAC and WavPack)
- multiple playlists
- automatic charset detection for cue files and ShoutCast metadata
- playlist formats: m3u, pls, xspf
- ReplayGain support
- Last.fm/Libre.fm scrobbler
- CDDB support
- audio converter
- stream browser
- audio formats converter
- external programs execution on track change
- ReplayGain scanner
- archive reader
- audio recording
- visualization (spectre analyzer)
- global hotkeys
-
sox 14.4.2
Swiss army knife of sound processing.
'SoX' is a command line utility that can convert various formats of computer
audio files in to other formats. It can also apply various effects to these
sound files during the conversion.
As an added bonus, SoX can play and record audio files on several
unix-style platforms.
'SoX' is able to handle formats like Ogg Vorbis, MP3, WAV, AIFF, VOC, SND, AU,
GSM and several more.
Any format support requires at least libsox-fmt-base. Some formats have their
own package e.g. mp3 read and write support is provided by libsox-fmt-mp3.
'SoX' supports most common sound architectures i.e. Alsa, Libao, OSS and Pulse
(respectively provided by libsox-fmt-alsa, libsox-fmt-ao, libsox-fmt-oss and
libsox-fmt-pulse). It also supports LADSPA plugins.
-
timidity 2.14.0
Software sound renderer (MIDI sequencer, MOD player).
'TiMidity++' is a very high quality software-only MIDI sequencer and MOD player.
'TiMidity++' uses sound fonts (GUS-compatible or SF2-compatible) to render MIDI files,
which are not included in this package.
* Plays MIDI files without any external MIDI instruments at all
* Understands SMF, RCP/R36/G18/G36, MFI, RMI (MIDI)
* Autodetects and supports GM/GS/XG MIDI
* Understands MOD, XM, S3M, IT, 699, AMF, DSM, FAR, GDM,
IMF, MED, MTM, STM, STX, ULT, UNI (MOD)
* Does MOD to MIDI conversion (including playback)
* Outputs audio into various audio file formats: WAV, au, AIFF,
Ogg (Vorbis, FLAC, Speex)
* Supports JACK, ALSA and AO drivers
* Uses Gravis Ultrasound compatible patch files and SoundFont2 patch
files as the voice data for MIDI instruments
* Supports playing from archives (zip, lzh, tar...).
* Timidity++ can be used as an ALSA sequencer device
VIDEO apps:
-
byzanz 0.3.0
'Byzanz' is a desktop recorder and command line tool allowing you to
record your current desktop or parts of it to an animated GIF,
Ogg Theora, Flash or WebM.
'Byzanz' also allows recording of audio, when the output format supports it.
-
gst123 0.3.5
The program 'Gst123' is designed to be a more flexible command line player in
the spirit of 'ogg123' and 'mpg123', based on GStreamer.
gst123 plays all file formats supported by GStreamer, so if you have
audio/video collections which contain different file formats, like
flac, ogg and mp3, you can use gst123 to play all your audio/video files.
-
guvcview 2.0.6
GTK+ base UVC Viewer.
'Guvcview' is a simple GTK+ interface for capturing and viewing video from
devices supported by the Linux UVC driver, like webcams.
-
oggvideotools 0.9.1
Toolbox for manipulating and creating Ogg video files.
Contains the following command line tools:
* oggCat - concatenates two ogg video files
* oggCut - extracts parts of an ogg file
* oggDump
* oggJoin - multiplexes ogg streams
* oggLength
* oggTranscode - resizes ogg files in multiple ways
* oggScroll
* oggSilence
* oggSlideshow - creates slideshows from pictures
* oggSplit - demultiplexes ogv files
* oggThumb - creates thumbnails from an ogg video file
-
photofilmstrip 3.7.2
Slideshow creator with Ken Burns effect.
Creates movies out of your pictures in just three steps.
First select your photos, customize the motion path and render the
video. There are several output possibilities for VCD, SVCD, DVD up to
FULL-HD and even 4k.
The effect of the slideshow is known as "Ken Burns". Comments of the
pictures are generated into a subtitle file. Furthermore audio files
can be specified to setup the background music for the slide show.
-
qstopmotion 2.4.1
Application for creating stop-motion animation movies.
Qstopmotion users will be able to create stop-motions from pictures imported
from a camera or from the harddrive and export the animation to
different video formats such as mpeg or avi.
-
recordmydesktop 0.3.8.1
Captures audio-video data of a Linux desktop session.
The application produces an ogg-encapsulated theora-vorbis file.
recordMyDesktop tries to be as unobstrusive as possible by proccessing only
regions of the screen that have changed.
-
smtube 18.3.0
SMTube is a stand-alone graphical application which allows one
to search and download Youtube videos.
Although it is part of the SMPlayer project, it can be used
with any multimedia player such as mpv, MPlayer, VLC, Totem
or Dragon Player.
-
vokoscreen-ng 3.0.2
Easy-to-use screencast creator.
vokoscreenNG can be used to record videos from computers screen, webcams,
external cameras, etc.
This graphical tool can produce educational videos,
live recordings of browser navigation, tutorials of installations, record
videoconferences, etc.
You can capture an alone video or video and sound.
This program can save files in some formats and use some codecs for video
and audio:
- Video: x264, VP8, H.264 (Intel GPU) and MPEG-2 (Intel GPU).
- Audio: vorbis, flac, opus and mp3.
- File : mkv, webm, avi, mp4 and mov.
vokoscreenNG is a modern full replacement for vokoscreen, both written by
Volker Kohaupt. The main difference is that vokoscreen uses ffmpeg as base,
while vokoscreenNG has been rewritten from scratch and is based in GStreamer.
-
webcamoid 8.6.1
A full-featured webcam capture application.
webcamoid allows one to capture, save and view a video stream. It also can
do a lot of funny things.
Features:
* GUI interface.
* Take pictures and record videos with the webcam.
* Many recording formats.
* Add funny effects to the webcam.
* +60 effects available.
* Effects with live previews.
* Use custom network and local files as capture devices.
* Capture from desktop.
* Manages multiple webcams.
* Custom controls for each webcam.
* Translated to many languages.
* Virtual webcam support for feeding other programs.
-
winff 1.5.5
Graphical video and audio batch converter using ffmpeg or avconv.
WinFF is a graphical user interface for FFmpeg or avconv.
It will convert almost any video file that FFmpeg or avconv will convert.
WinFF does multiple files in multiple formats at one time.
You can, for example, convert mpeg's, flv's, and mov's into
avi's (or DVD/VCD format or MPEG or 3gp etc.) all at once.
WinFF provides a variety of preset conversion settings for
common formats and devices. These presets are intended to hit the
"sweet spot" for each individual codec. They have been written with a
tip of the balance to quality.
For most presets to work, it is necessary to have the unstripped version
of the libavcodec package, which can be obtained by installing
libavcodec-extra as suggested by the WinFF suite. It might be necessary
to enable additional repositories to find that package.
'top' apps:
-
dnstop 20120611-2
Console tool to analyze DNS traffic.
'dnstop' is a console tool to analyze and display various tables
of DNS traffic.
Currently dnstop displays tables of (among others):
* Source IP addresses
* Destination IP addresses
* Query types
* Top level domains
* Second level domains
-
iftop 1.0
Displays bandwidth usage information on an network interface.
'iftop' does for network usage what top(1) does for CPU usage.
It listens to network traffic on a named interface and displays
a table of current bandwidth usage by pairs of hosts.
Handy for answering the question "Why is my Internet link so slow?".
-
iotop 0.6-24
Simple top-like I/O monitor.
'iotop' does for I/O usage what top(1) does for CPU usage.
It watches I/O usage information output by the Linux kernel and
displays a table of current I/O usage by processes on the system.
It is handy for answering the question "Why is the disk churning so much?".
'iotop' can only run under a Linux 2.6.20 or later kernel built with the
CONFIG_TASKSTATS, CONFIG_TASK_DELAY_ACCT, CONFIG_TASK_IO_ACCOUNTING and
CONFIG_VM_EVENT_COUNTERS build config options on.
FILE MANAGEMENT apps:
-
dirdiff 2.1-7.2
Display and merge changes between two directory trees.
'Dirdiff' can handle up to 5 trees. It displays a main window with a
list of the files which are different between the trees, with colored
squares to indicate the relative ages of the versions.
A menu allows you to display the differences between any two of
the versions in another window. Another menu allows you to copy
the file from one tree to another.
NETWORK MANAGEMENT apps:
-
etherape 0.9.18-2
Graphical network monitor.
'EtherApe' is a graphical network monitor modeled after 'etherman'.
'EtherApe' displays network activity graphically, showing active
hosts as circles of varying size, and traffic among them as
lines of varying width.
'EtherApe' features link layer, ip and TCP modes, color-coded protocols
display, Ethernet, FDDI, Token Ring, ISDN, PPP and SLIP devices.
'EtherApe' can filter traffic to be shown, and can read traffic from
a file as well as live from the network.
-
inetutils-traceroute 1.9.4-11
Trace the IPv4 route to another host.
The 'traceroute' utility displays the route taken by IP packets on their
way to another host or another network.
Install this package if you need a tool to examine network connectivity
or to diagnose network problems.
-
ipcalc 0.41-5
Parameter calculator for IPv4 addresses.
'ipcalc' takes an IPv4 address and netmask and calculates the resulting
broadcast, network, Cisco wildcard mask, and host range.
By giving a second netmask, you can design sub- and supernetworks.
'ipcalc' is also intended to be a teaching tool and presents the results
as easy-to-understand binary values.
Originally, 'ipcalc' was intended for use from the shell prompt, but a
CGI wrapper is provided to enable colorful HTML display through a
webserver. You can find the wrapper in '/usr/share/doc/ipcalc/examples' directory.
-
linssid 3.6-4
LinSSID is a graphical program that displays locally receivable 802.11
wireless attach points and ad hoc networks.
A table is displayed with various parameters such as MAC address, channel,
and signal strength. Graphs are also displayed with signal strength by
channel and signal strength over time.
LinSSID is graphically and functionally similar to inSSIDer (for Microsoft
Windows) and Wi-Fi Analyzer (for Android).
LinSSID can be used to measure the local performance or to search for an
interference free channel to be set in a wireless router (access point or
AP).
The wireless established link won't be affected by these operations
because LinSSID needn't set the monitor mode in network interface.
Some features:
- Table of locally receivable attach points with many columns of different
information and sortable and movable columns.
- Adjustable speed, real-time update.
- Graphs of signal strength by channel and over time.
- AP bandwidth displayed.
- Works on both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz channels.
-
pktstat 1.8.5-6
'top'-like utility for network connections usage.
'pktstat' displays a real-time list of active connections seen on a
network interface, and how much bandwidth is being used by what.
'pktstat' partially decodes HTTP and FTP protocols to show what
filename is being transferred, as well as X11 application names.
Entries hang around on the screen for a few seconds so you can
see what just happened.
'pktstat' also accepts BPF expressions.
-
tcptrack 1.4.2-2
TCP connection tracker, with states and speeds.
'tcptrack' is a sniffer which displays information about TCP connections
it sees on a network interface.
'tcptrack' passively watches for connections on the network interface,
keeps track of their state and displays a list of connections
in a manner similar to the unix 'top' command.
'tcptrack' displays source and destination addresses and ports, connection
state, idle time, and bandwidth usage.
-
traceroute 2.1.0-2
Traces the route taken by packets over an IPv4/IPv6 network.
The 'traceroute' utility displays the route used by IP packets
on their way to a specified network (or Internet) host.
'Traceroute' displays the IP number and host name (if possible)
of the machines along the route taken by the packets.
'Traceroute' is used as a network debugging tool. If you're having
network connectivity problems, 'traceroute' will show you where the
trouble is coming from along the route.
DOCUMENT apps:
-
evince 3.36.7
(Gnome PDF reader,
to augment MATE 'Atril')
Document (PostScript, PDF) viewer.
'Evince' is a simple multi-page document viewer.
'Evince' can display and print PostScript (PS), Encapsulated
PostScript (EPS), DjVu, DVI, Portable Document Format (PDF)
and XML Paper Specification (XPS) files.
When supported by the document, it also allows searching for text,
copying text to the clipboard, hypertext navigation, and
table-of-contents bookmarks.
COMPUTER SYSTEM MONTIORING apps:
-
dstat 0.7.4-6
Dstat is a versatile replacement for vmstat, iostat and ifstat. Dstat
overcomes some of the limitations of these programs and adds some
extra features.
Dstat allows you to view all of your network resources instantly, you
can for example, compare disk usage in combination with interrupts
from your IDE controller, or compare the network bandwidth numbers
directly with the disk throughput (in the same interval).
Dstat also cleverly gives you the most detailed information in columns
and clearly indicates in what magnitude and unit the output is displayed.
Dstat is also unique in letting you aggregate block device throughput for
a certain diskset or network bandwidth for a group of interfaces, i.e. you
can see the throughput for all the block devices that make up a single
filesystem or storage system.
-
gmemusage 0.2-11
Displays a graph detailing memory usage of each process.
'Gmemusage' is a graphical program modelled after the Silicon Graphics Inc.
program of the same name. 'Gmemusage' displays a window with a stacked bar.
Areas on the bar correspond to individual processes running on the system
and are updated periodically.
Multiple copies of the same program (actually, programs with the same name)
are merged into one area on the stack. Sizes of areas in the stack
correspond to resident sizes of the processes.
-
hardinfo 0.5.1
Displays system information.
'HardInfo' is a small application that displays information about your
hardware and operating system. Currently it knows about PCI, ISA PnP, USB,
IDE, SCSI, Serial and parallel port devices.
-
health-check 0.03.06
Health-check monitors processes and optionally their child
processes and threads for a given amount of time.
At the end of the monitoring it will display the CPU time used,
wakeup events generated and I/O operations of the given processes.
It can be used to diagnose unhealthy bad processes.
-
procinfo 2.0.304-3
Tools to display information from /proc and /sys.
The 'procinfo' package provides three small programs that gather
system information from diverse files under /proc and /sys and
print it to the screen:
* lsdev - information from /proc about installed hardware;
* procinfo - system monitoring statistics from /proc and /sys;
* socklist - a summary of open network sockets from /proc/net.
-
pstack 1.3.1
pstack dumps a stack trace for a process, given the PID of that process.
If the process named is part of a thread group, then all the threads
in the group are traced.
PHYSICS/ASTRONOMY apps:
-
planets 0.1.13-20
Gravitation simulation of planetary bodies.
'Planets' is a simple interactive program for playing with simulations
of planetary systems. It is great for teaching gravitation on planet
level.
The user interface is aimed at being simple enough for a fairly young
kid to enjoy it. There is a special kid-mode for this purpose.
-
xplanet 1.3.0-5.1
Planetary body renderer.
'Xplanet' renders an image of a planet into an X window or a file. All
of the major planets and most satellites can be drawn, and different
map projections are also supported, including azimuthal, hemisphere,
Lambert, Mercator, Mollweide, Peters, polyconic, and rectangular.
In order to run xplanet, you'll need at least one map file. Some maps
are included in the xplanet-images package.
OTHER apps:
-
hexdiff 0.0.53
Editor to visualize binary differences in hexadecimal between 2 files.
The editor opens in an horizontal split view with each file per view.
Each view has 3 columns : offset, hexadecimal output, ASCII output.
Differences are highlighted by having the background color inverted.
Some crucial information are displayed as current offset, etc.
Has shortcut to move into the file, to the next difference, etc.
-
linuxlogo 5.11-9
A Color ANSI Logo with some system information that can be
displayed at system boot time or, with some local configuration,
at the login prompt.
Four different Logos are available:
* Debian Swirl(default)
* Debian Banner
* Tux Classic
* Banner
-
smtm 1.6.11 ( = Show Me The Money )
smtm, a not overly clever acronym for Show Me The Money, is a
simple stock ticker and charting application. It creates and automatically
updates a window with stock quotes from Yahoo! Finance, as well as optional
charts from Yahoo! Finance.
smtm is configurable -- it can display the stock symbol and the full
name of the company, the price change, the percentage change, the volume
traded, the profit or loss, the value of the holding, the length of the
holding period, annualised percentage returns and more.
The display can be sorted on almost any of the columns.
Losers are flagged in red.
smtm can be used for most global stock symbols, North American
mutual funds and options, currencies and some commodities --
anything supported Yahoo! Finance.
Stock quotes are normally delayed, 15 minutes for NASDAQ and 20
minutes otherwise. See Yahoo! Finance for details.
MORE APPS THAT I-MAY-INSTALL:
(3 May 2021 update)
I used the Synaptic GUI package manager to look for even more 'apps'
that I might wish to install someday.
Here is a list - with a brief description of some of them. (This is
mostly to remind me of their existence and that I might want to
install them someday.)
The list is in alphabetical order, with the exception of the
first app.
-
cuneiform
mulit-language OCR system - which might be used as an alternative
to 'tesseract', above
-
admesh
tool for processing/fixing triangulated solid meshes (STL files)
-
atop
montior system resources & process activity
-
avogadro
molecular graphics & modelling system
-
ballview
free molecular modeling & molecular graphics tools
-
beep
advanced pc-speaker beeper
-
birdfont
font editor that lets you create outline vector graphics
& export fonts
-
caca-utils
text mode graphics utilities
-
efitools
tools for UEFI secure boot platforms
-
starplot
3D perspective star map viewer
-
tcptraceroute
a traceroute implementation using TCP packets
-
tetgen
a quality tetrahedral mesh generator
-
unhtml
remove the markup tags from an HTML file
-
usbtop
another 'top' command
-
usbview
USB device viewer
-
uvccapture
USB UVC snapshots
(UVC refers to 'USB Video Class' camera devices like webcams)
-
vbrfix
fix variable-bit-rate MP3 files
-
vgrabbj
grab image from webcam
-
viewmol
front end for some chemical programs
-
vlevel
audio filter
-
vmg
Virtual Magnifying Glass
-
vmpk
Virtual MIDI Piano Keyboard
(like 'vkeybd')
-
vnstat
network traffic monitor
-
vpx-tools
vp8, vp9 video codecs
(commands: vpxdec, vpxenc)
-
vuesz
2D, 3D scientific plotting
-
wallstreet
news to console
-
wavbreaker
splits WAVE audio files
-
wavemon
wireless device monitor
-
webp
lossy compression of photos
-
wise
compare biopolymers
-
yale
a star catalog (bright stars)
-
yatm
Yet Another Time Machine
(an audio file 'stretcher')
-
ytcc
You Tube Channel Checker
-
xdrawchem
-
xoscope
digital oscilloscope
And I may return to Synaptic to look for more.
PARTING GENERAL IMPRESSIONS:
I am favorably impressed by the stability and 'polish'
of the Ubuntu-MATE 20.04 'distro'.
But I am disgusted with the time I had to spend
solving the 'garbled desktop' problem and the
Realtek 8821ce wireless adapter problem.
To end on a somewhat brighter note:
After installing the many apps and utilities,
I saw that only about 13 GB of the 1 TB disk drive
was used --- by the operating system files and
the application files --- less than 2% of the disk
--- for several hundred thousand files.
There is plenty of room on the 1 TeraByte disk
for more apps and data.
Considering the massive amount of code and data in my
installation, and opportunities for bugs and flaws
to show up in all those files, I feel
very satisfied with the Ubuntu-MATE 20.04 installation on
this HP laptop.
This 'distro' feels very 'solid' in almost
all areas --- after the initial install problems were
solved.
|